The Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) is a crucial part of the financial aid process for students. Submitting this form helps make higher education more affordable and accessible, empowering students to seek their desired path for long-term success. Affordability is a primary concern for many students and families, so simplifying the financial aid process and enhancing student knowledge can significantly impact their actions and attitudes toward higher education. Here, you can discover the best ways to engage students and ensure their understanding of the FAFSA and other methods of covering the cost of education.
The FAFSA is critical for students needing financial support to cover the cost of higher education. This tool gathers essential information to determine which loans and grants a student qualifies for and contributes to lower student loans after graduation. The application is free to complete, and every student should complete it to receive personalized financial support. The FAFSA considers several aspects, including special circumstances, tax records, untaxed incomes such as child support, and other assets, to provide financial aid opportunities to make higher education more affordable.
Students can use FAFSA money for various educational purposes, including tuition, books, room, board, and other college or university fees. Students can complete yearly, updating their information and receiving accurate aid based on their current needs and family financial situation.
The financial award amount for each student is typically segmented throughout the academic year, meaning it does not come all at once. Funds appear based on the institution and the student’s enrollment. For example, students often receive half of their aid at the start of the Fall semester and again at the start of the Spring semester in traditional higher education environments.
The biggest advantage of completing the FAFSA is receiving money from the federal government that students, some of which they don’t need to repay. Student debt is a crippling factor for student dropouts, with nearly 40 percent of dropouts occurring due to financial concerns and pressure. With college tuition facing price increases, it is more vital now than ever before for students to complete the FAFSA to receive the necessary financial support.
The Pell Grant alone can deliver up to $7,395 of aid. While each student’s enrollment status, attendance cost, and family contributions will impact this amount, the bottom line is that this federal student aid can be the difference between empowering a student to pay for education rather than dropping out or neglecting to apply to an institution in the first place.
While the FAFSA plays a significant role in accessing affordable education, it can be beneficial to understand the overall financial aid process. There are several ways students can pay for college, and these financial awards often go hand in hand. However, many prospective students do not know where to begin applying for aid or how to access forms and documents to ensure they get the most aid possible. Generally, students should follow these steps:
A new FAFSA form launched in December 2023, bringing several significant changes for students and families. These changes transformed parts of the application process, making aid even more accessible for students. Institutions should understand these changes and encourage students to be prepared to:
With so many students and families relying on federal aid to make education accessible, it’s crucial to understand the do’s and don’ts of completing the FAFSA. Several common mistakes can prevent students from receiving financial awards. Communicating these mistakes and establishing the best completion tips can ensure students get the help they need.
Some of the most common oversights include:
Institutions can encourage students to follow these tips for FAFSA completion:
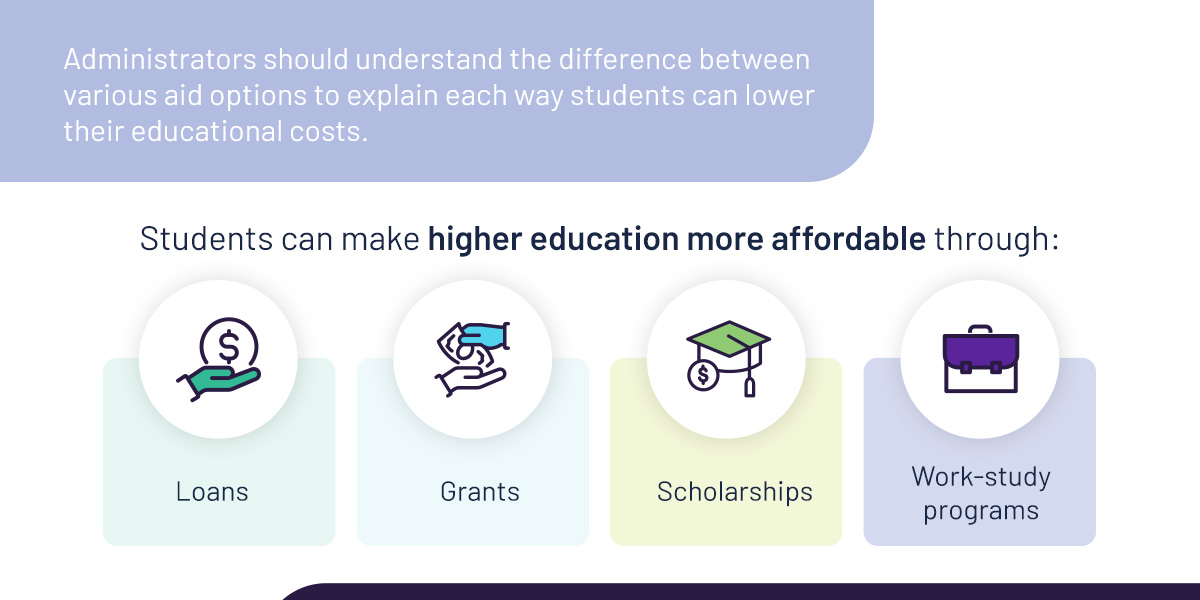
Administrators should understand the difference between various aid options to explain each way students can lower their educational costs. Students should understand what your institution offers and what combination of aid will be the most beneficial.
There are two primary types of aid. Merit-based aid is an institutional award providing aid to students with specific talents or academic, artistic or athletic abilities. These financial rewards vary by school, making some institutions more affordable than others. Need-based aid refers to monetary rewards students can obtain from the government and by completing the FAFSA.
Students can make higher education more affordable through:
Higher education institutions can take several steps to improve financial aid transparency and simplify the process for prospective students. Increasing conversations about this subject can spark greater interest in your community and empower students to seek the right program. Here’s how your institute can contribute to this collaborative culture:
Higher education institutions can take the reins by offering assistance programs. Many institutions have created engaging programs to help students and families navigate the financial aid process. From hosting regular seminars to building comprehensive support networks to throwing celebratory community events for FAFSA completion, there are many ways to spread financial aid information and ease the application completion process.
Increasing outreach efforts can bridge the gap between students and higher education institutions. Some students may not know where to begin searching for financial aid or understand the options available to them. Starting the conversation with engaging outreach can help them start the process and navigate applications in a timely manner.
While you can administer mass emails or papers, a more personalized approach is often more successful. Personalized mailings regarding free or lowered tuition may increase application and enrollment rates. Other strategies, such as text message interventions, can also be more effective in reaching younger students who may be less likely to sort through physical mail.
Leveraging automation and robust technology can empower you to refocus your financial aid team’s time. Comprehensive solutions can help you access base-level information quickly, allowing your team to provide a more tailored experience for each student. This technology can provide a comprehensive view of your financial package offers, student funding sources, and any balances due, enhancing communication and understanding on both sides.
Watermark is higher education’s got-to software suite for driving student success and meeting institutional goals. We empower continuous improvement by delivering high-quality solutions for simplifying workflows, enhancing communication, and boosting student engagement. Watermark products can help students overcome financial obstacles and make processes easier for students and administrators.
Watermark Student Success & Engagement delivers crucial insights for student engagement, optimizing degree completion, and increasing retention rates. Our predictive analytics software can identify at-risk students, empowering you to intervene at crucial moments. Our solutions also provide benefits by allowing actions such as completing forms, creating a central location for important documents, and enhancing communication with students.
When you need to engage students and optimize your retention and enrollment, trust Watermark to provide the quality solutions to transform your processes and give your students the tools they need to succeed. Request a demo of our Student Success & Engagement software to see what we can do for your institution.
























































































































































































































































































































































































Submit this form to schedule a meeting with one of our reps to learn more about our solutions. If you need customer support instead, click here.