




The workplace is changing at an unprecedented pace. Higher education institutions are implementing high-impact practices to ensure student learning prepares them for the workplace. Many have seen success with experiential learning, allowing students to experiment and draw meaning from the world.
Students who engage in experiential learning often have fulfilling careers, which is just one of the model’s many benefits. However, integrating experiential learning opportunities into your curriculum requires planning. In this practical guide to mapping experiential learning, you’ll learn how to derive maximum value for your students, faculty, and institution.
In simple terms, experiential learning is the process of learning by doing. It involves engaging students in hands-on experiences and connecting theories they learn in the classroom with practical applications. Experiential learning theory, developed by David A. Kolb, outlines the ideal learning process in a four-step cycle:
This experiential learning cycle mirrors the natural learning we experience in many situations. It offers several benefits, including:

Curriculum mapping establishes the link between course content and expected student learning outcomes. It involves aligning teaching activities, learning goals, and assessment methods with desired educational objectives. It creates a more integrated and coherent curriculum and guides faculty to ensure that courses stay on track with student outcomes. Curriculum mapping also helps you create educational programs that meet the experiential learning outcomes that students need to succeed.
Some of the many ways curriculum mapping supports experiential learning include:
Curriculum mapping helps you identify the core competencies and learning outcomes that each student should achieve. You can define competencies based on the desired skills and abilities necessary for success in experiential learning. One skill builds on the other, ensuring a logical and sequential progression of competencies. Students can build on their abilities progressively, mastering the basics before moving on to the next learning stage.
A curriculum map ensures that experiential learning doesn’t happen in a vacuum. Instead of being incidental, it’s aligned with academic standards, accreditation requirements, and industry expectations. It solidifies the connection between theoretical learning and practical application while ensuring that every element of your curriculum works as a cohesive whole.
When you can see your entire curriculum mapped out, it’s easier to identify improvement opportunities. You can see where students aren’t learning what they need from experiential opportunities and pinpoint areas where you can add more. Experiential learning is only meaningful if it relates to overarching learning outcomes. With curriculum mapping, you can ensure that every activity contributes to long-term student goals, making every experience more meaningful for students.
Although experiential learning is a process of trial and error, you still need a way to assess whether students meet the desired outcomes. Curriculum mapping streamlines the alignment of assessments and evaluations with the identified competencies. It helps ensure that your chosen assessment measures each student’s practical skill mastery. You can track and evaluate student progress, allowing students to draw their own conclusions and providing personalized feedback and support for improvement.
With the right tools, your institution can complete curriculum mapping digitally. Faculty members who use curriculum mapping solutions in the same department can access each other’s plans. They communicate to ensure that students leave their classes with similar theoretical and practical knowledge. Faculty can also collaborate across departments to ensure students receive a holistic education.
Students and faculty know what to expect so they can use and allocate resources effectively, identify redundancies, and address gaps in the learning experience. A curriculum map also provides data and insights into the effectiveness of experiential learning, allowing you to analyze student assessment and performance data to identify areas for improvement. It’s an iterative process that ensures your experiential learning programs remain responsive to changing student and workforce needs.
Creating an experiential learning curriculum requires a specialized approach. It requires faculty to give students more responsibility and autonomy over their learning. It also requires you to allocate resources and foster partnerships with local businesses and communities to provide students with meaningful experiential opportunities.
An experiential learning curriculum map is a comprehensive plan that supports students and faculty on the route to course completion. These maps help students explore majors and reflect on the career-relevant skills they gain, get hands-on job preparation, and engage in relevant job preparation.
Some of the steps you can take to create an experiential learning curriculum include:
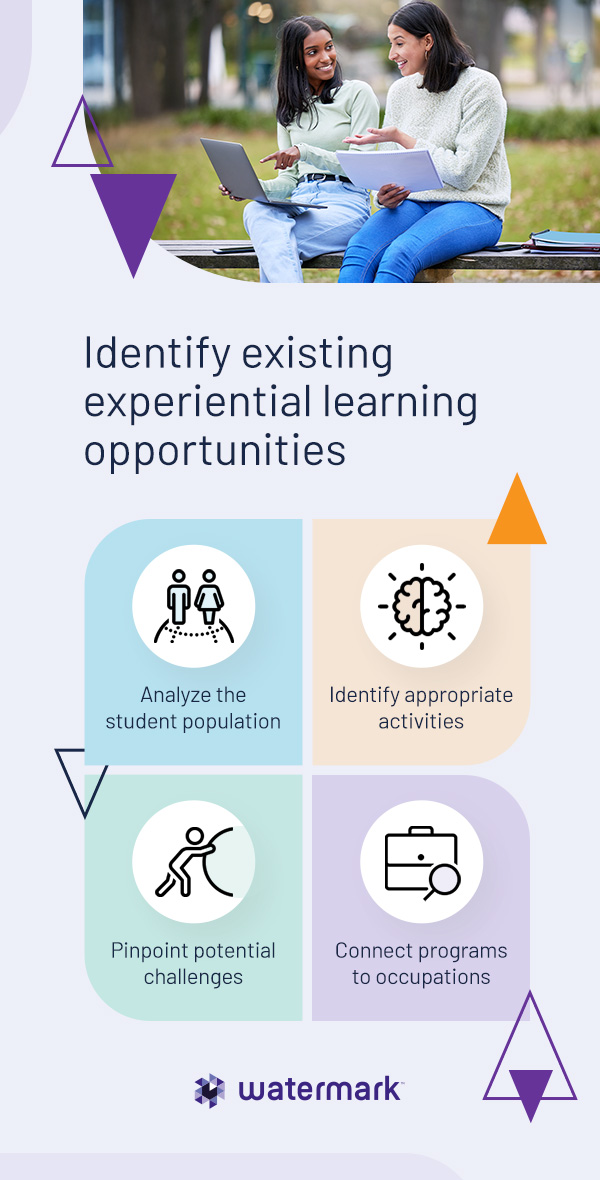
The first step in mapping experiential learning to outcomes is to identify the most meaningful experiences for students. As you begin the planning process, there are several steps you can take to identify experiential learning opportunities:
Depending on your resources and course content, you can integrate any of the following experiential learning opportunities:
When choosing experiential learning opportunities, the higher the student involvement, the more ownership and empowerment you’ll see. Encourage students to respond naturally to their environments and provide feedback on the outcomes so you can continue iterating and refining your processes.
Every experiential learning opportunity should lead to quantifiable student development. Before launching an experiential learning program, engaging in outcome mapping is essential. Establish learning outcomes and make them contextually relevant. Regardless of the type of experiential learning, you can create learning outcomes that cover students’ theoretical understanding, practical application, and reflection.
These experiences become more meaningful to students if you reinforce the learning with reflection and metacognition — thinking about their thoughts. Although experiential learning outcomes must be measurable, rote responses may not provide the right experience. Use a combination of written, visual, narrative, and interpersonal reflection to make learning more engaging and effective.
Some tips for aligning experiential learning with student outcomes include:
Experiential learning works best when it integrates seamlessly into your curriculum. A comprehensive curriculum map allows you to identify gaps, meet institutional objectives, and provide students with the relevant skills. Using purpose-built software solutions, you can see all your data in one place and quickly determine how experiential learning fits into your curriculum.
Some tips for creating a comprehensive curriculum include:

Curriculum mapping is a dynamic framework for continuous improvement that allows you to refine your course offerings in line with changing student needs. Once you have a completed curriculum map, follow these simple tips:
Experiential learning is designed to give students an idea of what to expect in the workplace, which includes interdepartmental collaboration. You can embed experiential learning across disciplines, from service-learning projects in liberal arts to capstone internships in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM).
Providing students with interdisciplinary opportunities helps them develop competencies and outcomes like communication, cooperation, and cultural awareness. They must communicate with diverse audiences and encourage collaboration between disciplines, as they would in the workplace.
As the workplace changes and employers emphasize skills over theoretical knowledge, experiential learning undeniably creates a cohesive, institution-wide strategy for student success. It’s a model that benefits everyone, from students and faculty to the institution and future employers. Staying agile in the face of a changing higher education landscape means embracing experiential learning to offer future student generations more engaging, practical, and relevant learning.
Mapping experiential learning into your curriculum gives students the hands-on education they need to succeed in the workplace. With the right curriculum mapping tools, you can simplify and streamline the process. Watermark Curriculum Strategy provides visual workflows to map out processes, reduces duplicate data entry, and ensures course consistency across departments.
Use student feedback to inform curricular changes and collaborate with all stakeholders to build a curriculum that drives student success. Request a demo of our solutions today!

























































































































































































































































































































































































Submit this form to schedule a meeting with one of our reps to learn more about our solutions. If you need customer support instead, click here.